PUMA-mediated copanlisib-induced apoptosis. A WT and PUMA-KO HCT116... | Download Scientific Diagram

Regulation of p53 Stability and Function in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

A p53/lnc‐Ip53 Negative Feedback Loop Regulates Tumor Growth and Chemoresistance - Zhang - 2020 - Advanced Science - Wiley Online Library

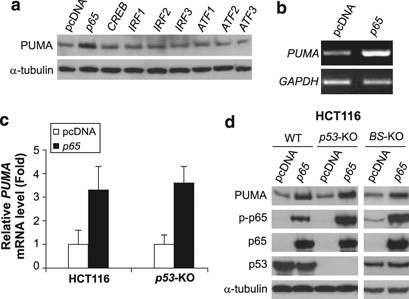
Inhibiting oncogenic signaling by sorafenib activates PUMA via GSK3β and NF-κB to suppress tumor cell growth | Oncogene
The Multi-Targeted Kinase Inhibitor Sunitinib Induces Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cells via PUMA | PLOS ONE
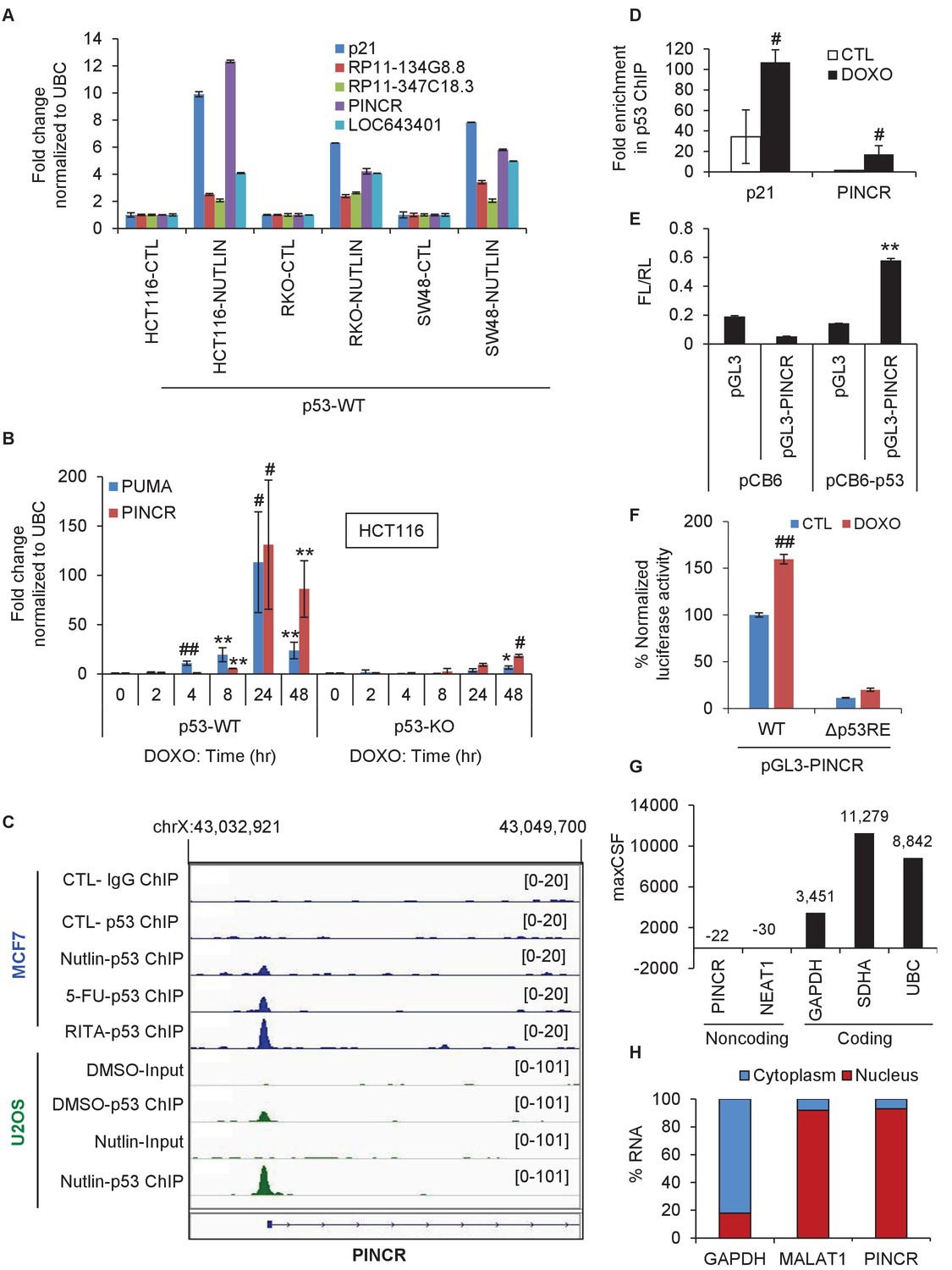
Figures and data in Prosurvival long noncoding RNA PINCR regulates a subset of p53 targets in human colorectal cancer cells by binding to Matrin 3 | eLife

A, p53-KO HCT116 cells were incubated with aciculatin (5–10 µM) for 48... | Download Scientific Diagram

Inhibiting oncogenic signaling by sorafenib activates PUMA via GSK3β and NF-κB to suppress tumor cell growth | Oncogene
Molecular crosstalk between ferroptosis and apoptosis: emerging role of ER stress-induced p53-independent PUMA expression

Wild-Type p53 Promotes Cancer Metabolic Switch by Inducing PUMA-Dependent Suppression of Oxidative Phosphorylation - ScienceDirect

Regulation of p53 Stability and Function in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells* - Journal of Biological Chemistry
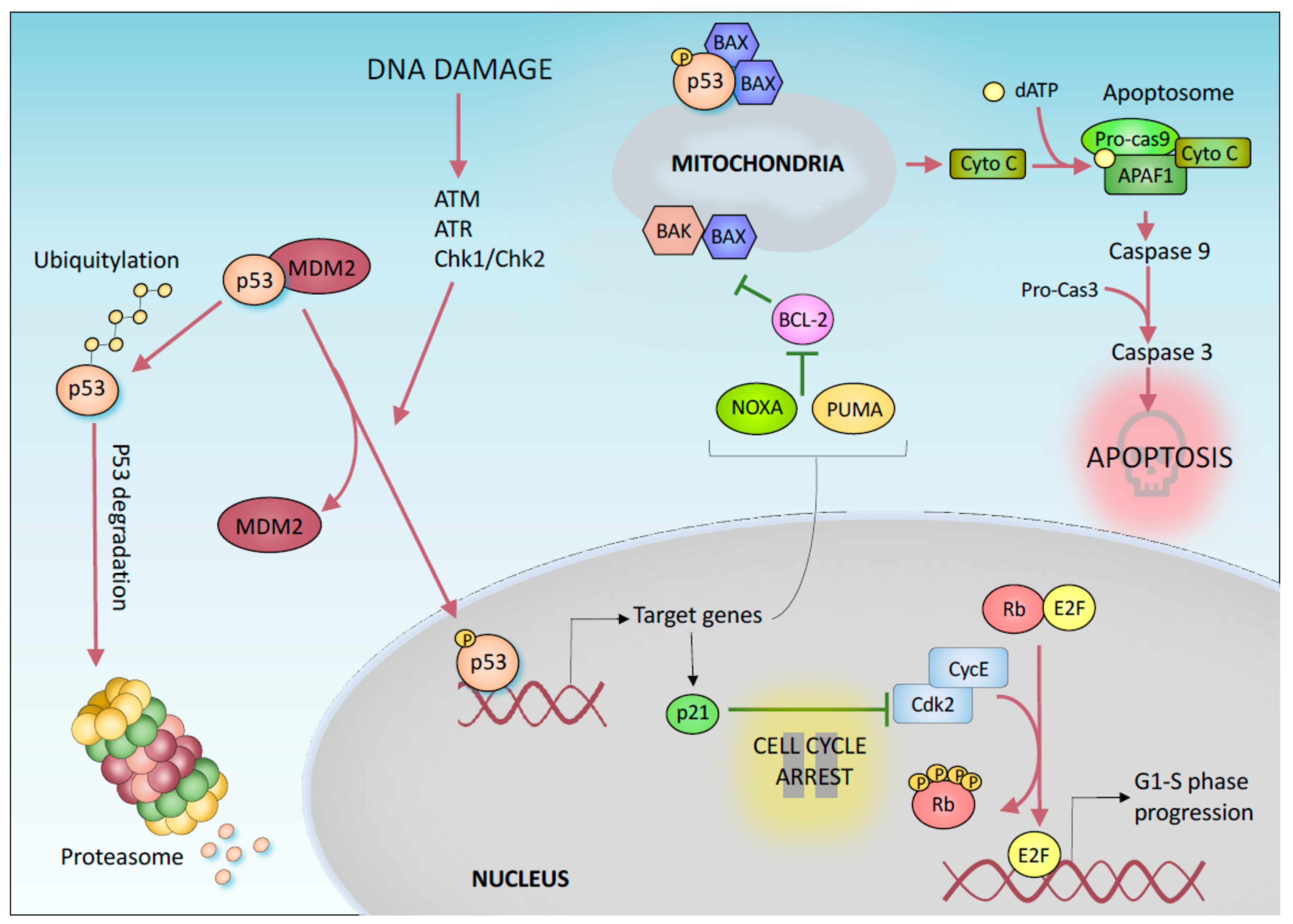
Cancers | Free Full-Text | p53-Mediated Tumor Suppression: DNA-Damage Response and Alternative Mechanisms | HTML
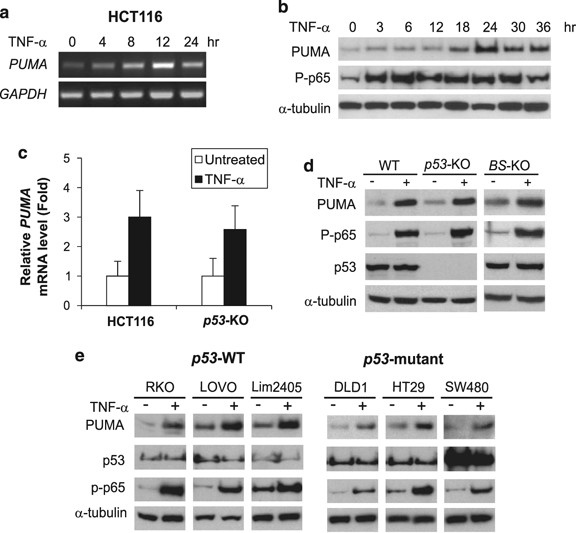
PUMA is directly activated by NF-κB and contributes to TNF-α-induced apoptosis | Cell Death & Differentiation

p300 regulates p53-dependent apoptosis after DNA damage in colorectal cancer cells by modulation of PUMA/p21 levels | PNAS